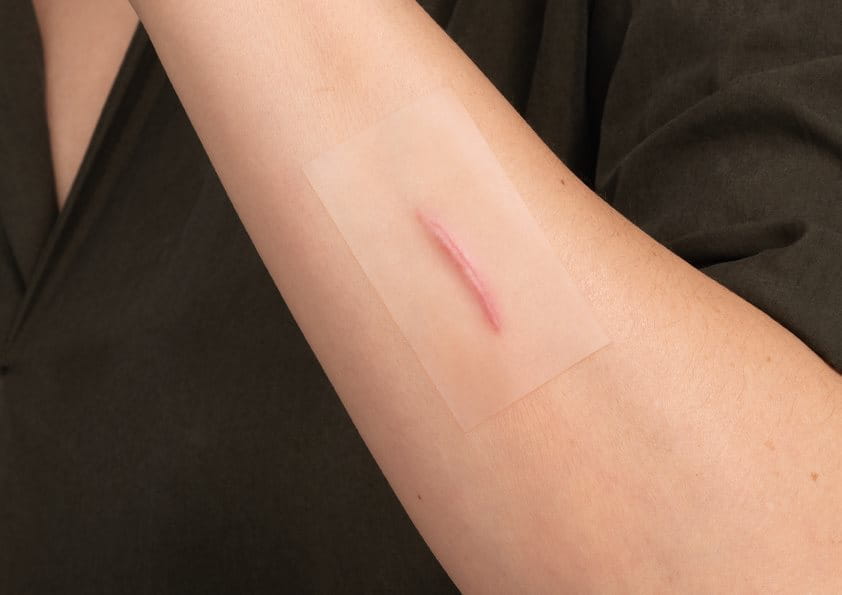
A fall down the stairs, a car accident or surgery: many of life’s events leave their marks as small or large scars. Nearly everybody has one or even more scars to remind him or her of such situations. Scars may not only cause discomfort and pain or hinder mobility, but can also reduce self-confidence particularly when located on visible parts of the body.
How do scars form?

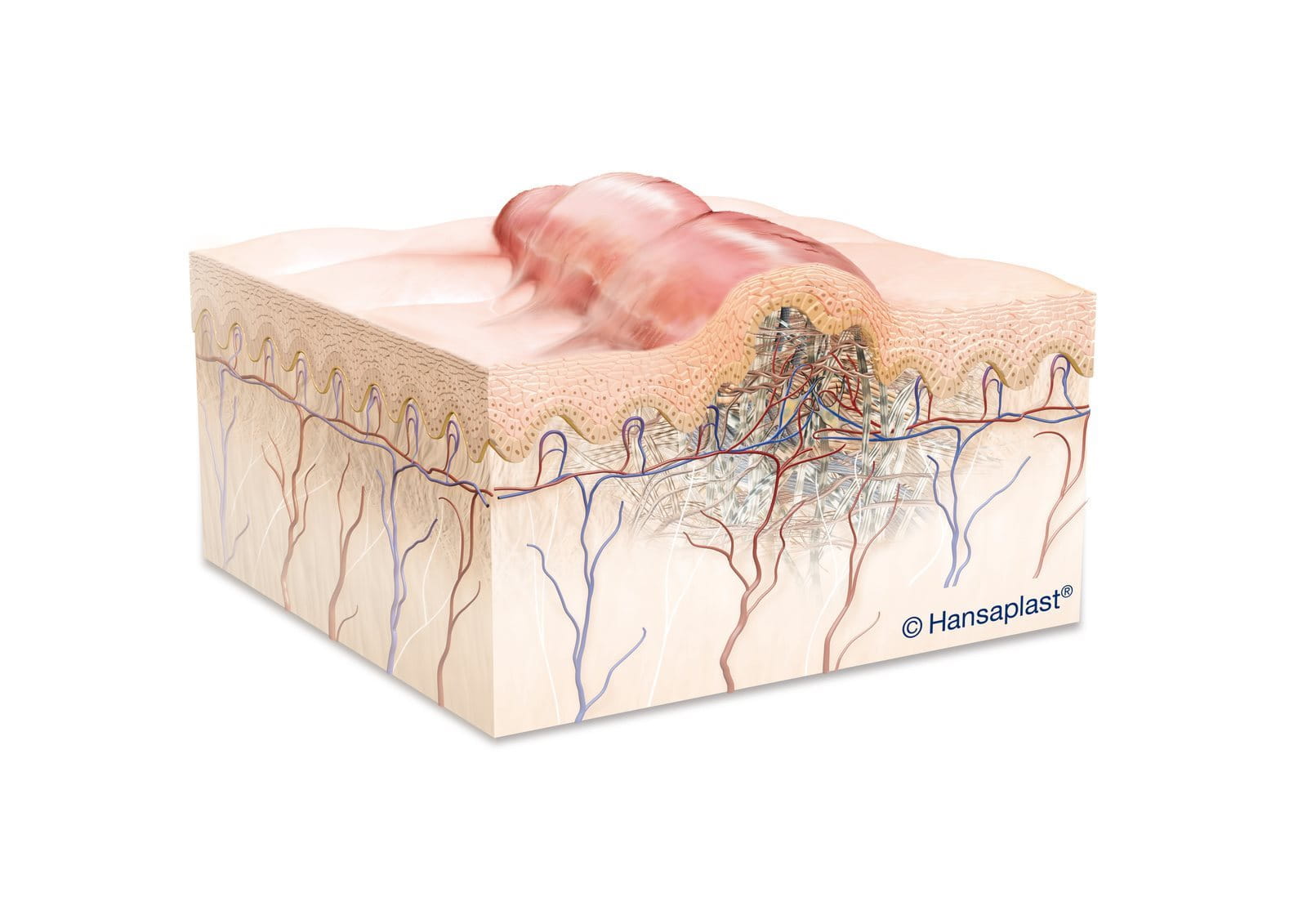
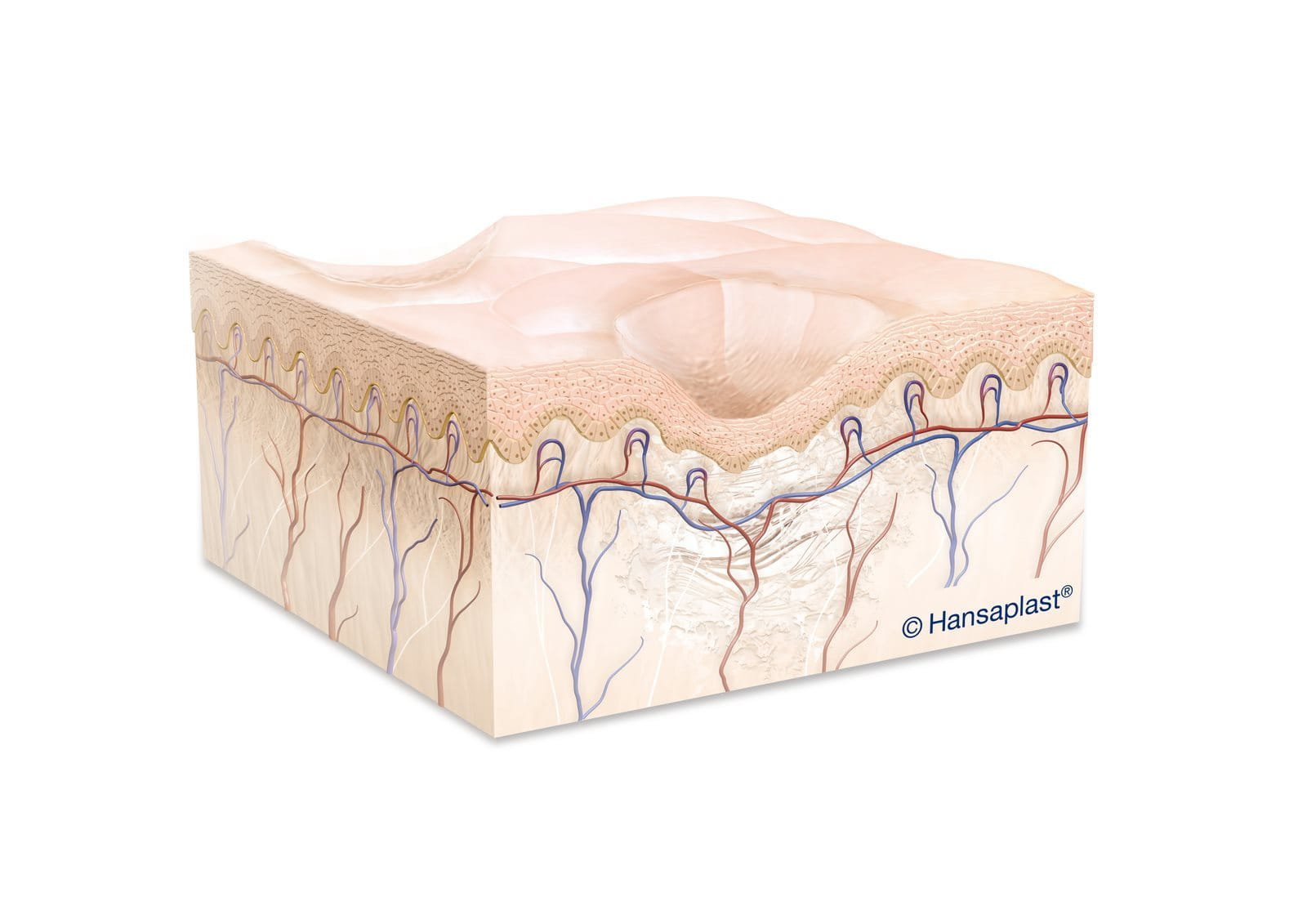
Scarring is a natural part of the healing process after a skin injury has been sustained. Only wounds that do not affect the dermis can heal without scars. As the organism is not able to replace the destroyed, highly specialised tissue in the same way, it repairs the wound with a fibrous connective collagen tissue to ‘bind’ the broken skin together. Even after the wound has healed, the body continues to direct collagen to the injury site, resulting in changes to the size and shape of the scar overtime. The so-called “maturation” phase can take years. Although most scars can’t be removed completely, there are steps that you can take to ensure a more even healing of your wound and reduce the visibility of existing scars. Learn more about wound healing here.